Unveiling the Power of Neuromarketing: A Guide to Understanding and Leveraging Consumer Behavior.
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced world, where consumers are bombarded with an overwhelming amount of information and choices, businesses are constantly seeking innovative ways to capture their audience’s attention and influence their purchasing decisions. One such revolutionary approach that has gained significant traction is neuromarketing. In this article, we will delve into the meaning, examples, strategies, and benefits of neuromarketing, shedding light on how it’s transforming the landscape of advertising and consumer behavior.
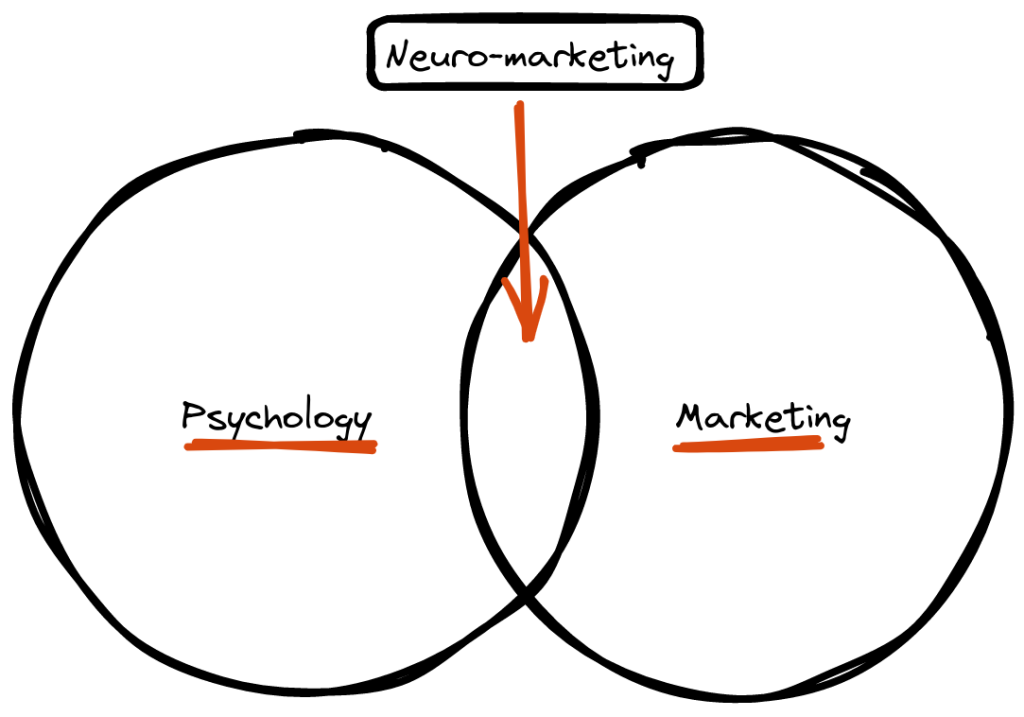
What is the Meaning of Neuromarketing?
Neuromarketing is the intersection of neuroscience and marketing, a multidisciplinary field that taps into the power of brain science to understand how consumers make decisions and respond to marketing stimuli. By studying brain activity, physiological responses, and subconscious reactions, businesses gain insights into the emotional and cognitive processes that drive consumer behavior. This knowledge enables them to tailor their marketing strategies for maximum impact.
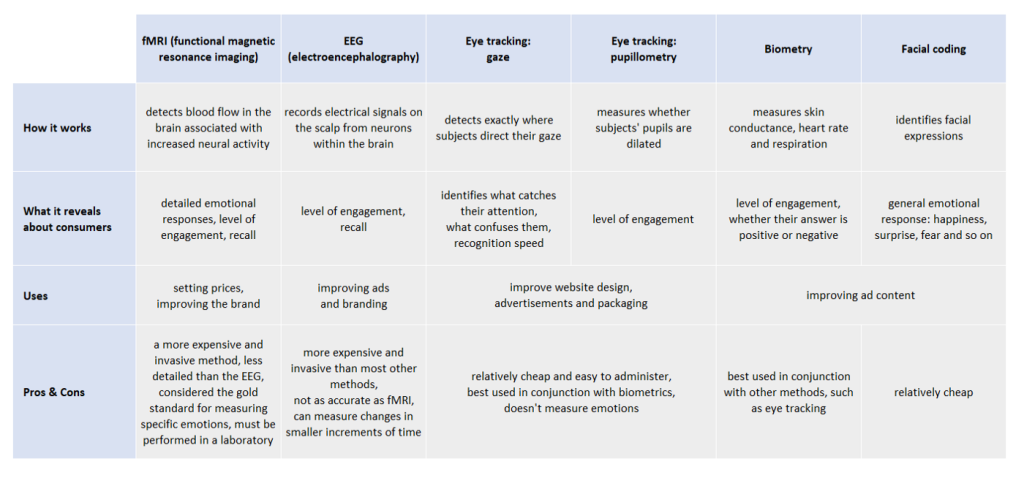
Using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electroencephalography (EEG), neuromarketing tracks brain activity, so businesses better understand their customers.
Neuromarketing Examples: Unmasking the Science Behind Success
1.Color Psychology: Brands often use specific colors to evoke emotions and associations. For instance, the color red might trigger a sense of urgency or excitement, which is why it’s commonly used in clearance sales or fast-food logos.
Red: Evokes urgency, excitement, passion, and can stimulate appetite. Often used in clearance sales and fast-food logos.
Blue: Conveys trust, calmness, and professionalism. Frequently used by tech companies and financial institutions.
Yellow: Represents optimism, cheerfulness, and warmth. Commonly found in branding for children’s products and sunshine-related businesses.
Green: Symbolizes nature, growth, and tranquility. Used by Eco-friendly and health-related brands.
Purple: Signifies luxury, creativity, and spirituality. Often chosen by beauty and high-end fashion brands.
Orange: Creates a sense of energy, enthusiasm, and warmth. Used by brands seeking to appear friendly and approachable.
Pink: Evokes feelings of love, femininity, and playfulness. Commonly used in products targeted at a female audience.
Black: Represents sophistication, power, and elegance. Frequently found in luxury and high-end fashion branding.
White: Symbolizes purity, simplicity, and cleanliness. Used in healthcare and minimalist branding.
Brown: Conveys reliability, earthiness, and ruggedness. Commonly used in outdoor and adventure-related branding.
2.Eye-Tracking Studies: Tracking where a person’s eyes focus on a visual stimulus can reveal which elements of an advertisement or product packaging draw the most attention. This insight informs marketers about what to emphasize or adjust.
3.Storytelling: Narratives have the power to engage our brains on multiple levels. Neuromarketing explores how storytelling activates various brain regions, making the content more memorable and relatable.
4.Social Proof: Seeing others enjoy a product can trigger a sense of belonging and influence purchasing decisions. This is evident in online reviews, testimonials, and even in the number of social media likes and shares.
5.Scarcity and Exclusivity: Creating a perception of scarcity or exclusivity taps into the brain’s fear of missing out (FOMO), motivating consumers to act quickly before a product or offer disappears.
Neuromarketing Tools and Measurement: Decoding Consumer Responses in Real Time
In the dynamic realm of marketing, where every second counts, the ability to capture and analyze consumer responses in real time is a game-changer. This is where neuromarketing tools and measurement come into play. These tools, often rooted in cutting-edge technology, provide marketers with invaluable insights into the subconscious reactions and emotions of their audience. Let’s delve into how these tools contribute to the world of neuromarketing and what advantages they bring to the table.
Understanding Neuromarketing Tools
1. EEG (Electroencephalography): This tool measures brainwave activity, enabling marketers to gauge the intensity of emotional responses to different stimuli. It offers a window into the viewer’s engagement level, guiding decisions on what elements of an ad require enhancement.
2. Eye-Tracking Technology: By tracing eye movement patterns, marketers identify precisely where the viewer’s attention is focused. This aids in optimizing visual content, ensuring that key messages and visuals capture the audience’s gaze.
3. Facial Expression Analysis: Advanced software interprets facial expressions to gauge emotional reactions such as joy, surprise, or frustration. This allows for adjustments in real time to elicit desired emotional responses.
4. Biometric Sensors: Heart rate and skin conductivity sensors offer insights into the viewer’s physiological responses. Changes in heart rate or skin conductance can signal emotional engagement, helping marketers fine-tune their content.
Advantages of Neuromarketing Tools and Measurement
Immediate Feedback: Traditional market research often relies on post-engagement surveys, but neuromarketing tools offer immediate, unbiased feedback during the viewing experience.
Accurate Insights: These tools tap into the subconscious, providing insights that consumers may not be able to articulate. This accuracy informs decisions that resonate with consumers on a deeper level.
Real-Time Adjustments: Marketers can make on-the-fly adjustments based on real-time data, ensuring their content is optimized for maximum impact.
Personalized Marketing: The granular insights from these tools allow for highly personalized marketing strategies tailored to individual responses.
Data-Driven Campaigns: Neuromarketing tools empower marketers with quantifiable data, enhancing the overall effectiveness of campaigns.
Conclusion
Neuromarketing tools and measurement elevate marketing strategies to new heights by offering an unprecedented glimpse into the minds and emotions of consumers. This real-time insight enables marketers to refine their approaches, ensuring that their messages resonate on a visceral level. As technology continues to evolve, the integration of these tools in the neuromarketing landscape will likely become even more sophisticated, leading to more effective and emotionally resonant campaigns.
How is Neuromarketing Used in Advertising?
Neuromarketing techniques have revolutionized the way advertisements are created and presented:
Neuroimaging: Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) and Electroencephalography (EEG) are used to monitor brain activity, helping marketers identify which elements of an ad trigger the most engagement.
Biometric Measurements: Heart rate, facial expressions, and even sweat response can reveal emotional reactions to ads, providing insights into the effectiveness of different visual and auditory stimuli.
Subliminal Messaging: While controversial, subtle cues inserted into advertisements can influence consumers’ decisions without their conscious awareness.
Product Placement: Neuromarketing uncovers the optimal placement of products within visuals, considering factors like gaze direction and visual flow.
Neuro-Design: Packaging, logos, and website design are crafted based on neuroscientific principles to trigger specific emotions and associations.

The Strategy of Neuromarketing: Decoding Consumer Behavior
Understanding the Brain’s Decision-Making Process: By studying how the brain evaluates options and weighs pros and cons, marketers can tailor messages to align with consumers’ thought processes.
Creating Emotional Connections: Neuromarketing emphasizes the importance of emotions in decision-making. Brands that evoke positive emotions are more likely to be remembered and recommended.
Simplicity and Clarity: The brain prefers easy-to-process information. Neuromarketing encourages clear messaging and simple visuals that the brain can quickly understand.
Personalization: Personalized marketing appeals to the brain’s innate need for relevance, increasing the likelihood of engagement and conversion.
Tapping into the Subconscious: Many decisions are made at a subconscious level. Neuromarketing leverages this by using subtle cues to influence behavior without conscious resistance.
Benefits of Neuromarketing: Unlocking Success for Businesses
- Enhanced Understanding of Consumers: Neuromarketing provides a deeper comprehension of consumer preferences, enabling businesses to fine-tune their offerings.
- Higher Conversion Rates: By tailoring marketing messages to resonate with the brain’s emotional centers, businesses can boost conversion rates and sales.
- Improved Brand Loyalty: Creating positive emotional associations with a brand through neuromarketing can foster long-term customer loyalty.
- Optimized Product Development: Insights from neuromarketing research can guide the development of products that align with consumers’ subconscious desires.
- Data-Driven Strategies: Neuromarketing adds a scientific dimension to marketing strategies, allowing businesses to make data-driven decisions backed by neuroscientific evidence.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving landscape of marketing, staying ahead of the curve is paramount. Neuromarketing offers a scientific approach to understanding consumer behavior and tailoring strategies that resonate deeply with audiences. By leveraging insights from brain science, businesses can create more impactful advertisements, forge stronger emotional connections with consumers, and ultimately achieve greater success in an increasingly competitive marketplace. Embracing the power of neuromarketing is not just a trend – it’s a transformational step toward unlocking the full potential of your marketing endeavors.